Why Tech Giants Embrace Standalone App Failures as a Strategy
In the fast-paced world of tech innovation, major players like Facebook, Instagram, and Dropbox are increasingly turning to standalone apps as experimental playgrounds. While these apps often fail to gain traction, they serve a crucial strategic purpose that many observers miss.
The Innovation Dilemma: Risk vs. Reward
Tech giants face a fundamental challenge: how to innovate without disrupting their core products that serve billions of users. As Facebook Product Manager Michael Reckhow explained, moving a billion people’s digital “furniture” is terrifying. This fear has led to the standalone app boom, where companies test new concepts in separate applications.
Why Core Apps Resist Change
- User experience preservation: Radical changes to main apps risk alienating existing users
- Feature burial risk: New features often get lost in complex existing interfaces
- Design constraints: Established apps must maintain consistent navigation schemes
The Standalone App Advantage
These experimental apps function like free plays in football - high-risk attempts with minimal consequences. They offer three key benefits:
- Low-cost experimentation: Small teams can develop concepts quickly
- Market testing: Real-world feedback without core product disruption
- Talent retention: Provides creative outlets for top engineers and designers
Notable Standalone Case Studies
| App | Parent Company | Outcome | Key Learnings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Facebook Paper | Limited adoption | Validated preference for traditional News Feed | |
| Instagram Bolt | Mixed results | Tested speed-focused messaging | |
| Dropbox Carousel | Dropbox | Declining usage | Explored photo backup solutions |
| Twitter #Music | Shut down | Gained music sharing insights |
The Acquisition Alternative
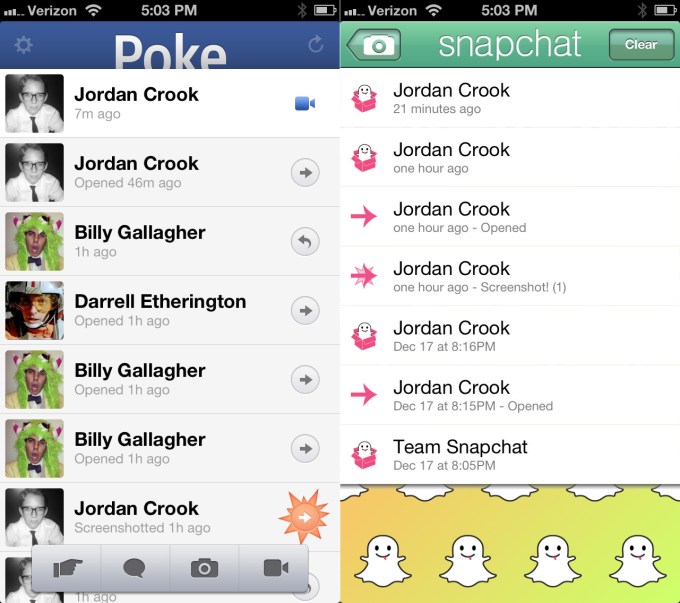
Standalone apps also serve as defense against disruptive startups. When Facebook failed to innovate in mobile photo sharing, it had to acquire Instagram for \(1 billion. Similarly, Snapchat's ephemeral messaging success forced Facebook to attempt a \)3 billion acquisition after its Poke clone failed.
Measuring Standalone App Success Differently
Rather than judging these apps purely by user numbers, consider their strategic value:
- Feature testing: Facebook Camera pioneered multi-shot uploads later adopted in main app
- Market intelligence: Twitter #Music provided valuable data on music sharing behaviors
- Talent development: Creative Labs initiatives foster innovation culture
- Competitive hedging: Slingshot represents a play against Snapchat’s dominance
Why Failure Is Acceptable
For tech giants, standalone apps represent calculated risks with:
- Minimal financial impact: Development costs are trivial relative to company size
- Limited brand damage: Failures don’t significantly affect core products
- Valuable learnings: Even unsuccessful apps generate actionable insights

The Future of Standalone Strategies
As the tech landscape evolves, we can expect:
- More frequent experimentation with standalone concepts
- Faster iteration based on market feedback
- Strategic acquisitions to complement successful experiments
- Continued press scrutiny despite the intentional high-failure-rate model
Rather than mocking standalone app failures, the tech industry should recognize them as smart, low-risk innovation strategies. In an environment where the cost of missing the next big trend far outweighs development expenses, these experimental apps represent sound business decisions.












